What is 3D Dental Imaging?
- What is 3D Dental Imaging and How Does it Differ from Conventional X-Rays?
- Why Should I Choose 3D Dental Imaging for Dental Procedures?
- What Are the Key Benefits of 3D Dental Imaging in Dentistry?
- How Can Dentists Incorporate 3D Dental Imaging Into Routine Dental Care?
- What is Cone Beam CT (CBCT)?
- Does My Insurance Cover 3D Dental Imaging?
- How Do You Benefit from 3D Dental X-Rays?
- How to Do 3D Imaging?
- What is the Purpose of 3D Imaging?
- Types of 3D Imaging for Dental Care
- FAQ

What is 3D Dental Imaging and How Does it Differ from Conventional X-Rays?
3D dental imaging, also referred to as dental 3D imaging, uses cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) to produce high-resolution, volumetric images of the oral cavity. Unlike traditional 2D x-rays that offer flat and limited visuals, 3D imaging dental technology delivers a full, three-dimensional perspective, allowing dentists to examine teeth, jawbones, nerves, and soft tissues in precise detail.
Traditional x-rays often require multiple angles to approximate depth, whereas 3D dental imaging software captures a complete dataset in a single scan. This not only improves diagnostic capabilities but also reduces the risk of missing underlying issues. With the use of 3D imaging software dental, practitioners can better plan procedures such as implant placements or extractions. For patients, this means fewer surprises, more predictable outcomes, and greater peace of mind.Why Should I Choose 3D Dental Imaging for Dental Procedures?
Choosing 3D dental imaging enhances the accuracy and success rate of dental treatments. It enables dentists to visualize oral structures in all dimensions, which is crucial for planning complex procedures like implant placements, root canal treatments, and orthodontics. This advanced level of insight leads to more personalized and effective care.
Additionally, dental 3D imaging software significantly reduces radiation exposure by targeting only specific areas, making it a safer option compared to traditional radiography. The clarity provided by these scans answers the question, “what does 3D dental imaging show?”—from hidden decay to bone abnormalities, everything is made visible. When combined with 3D imaging in dental implantology, this approach leads to safer surgeries and more confident decisions.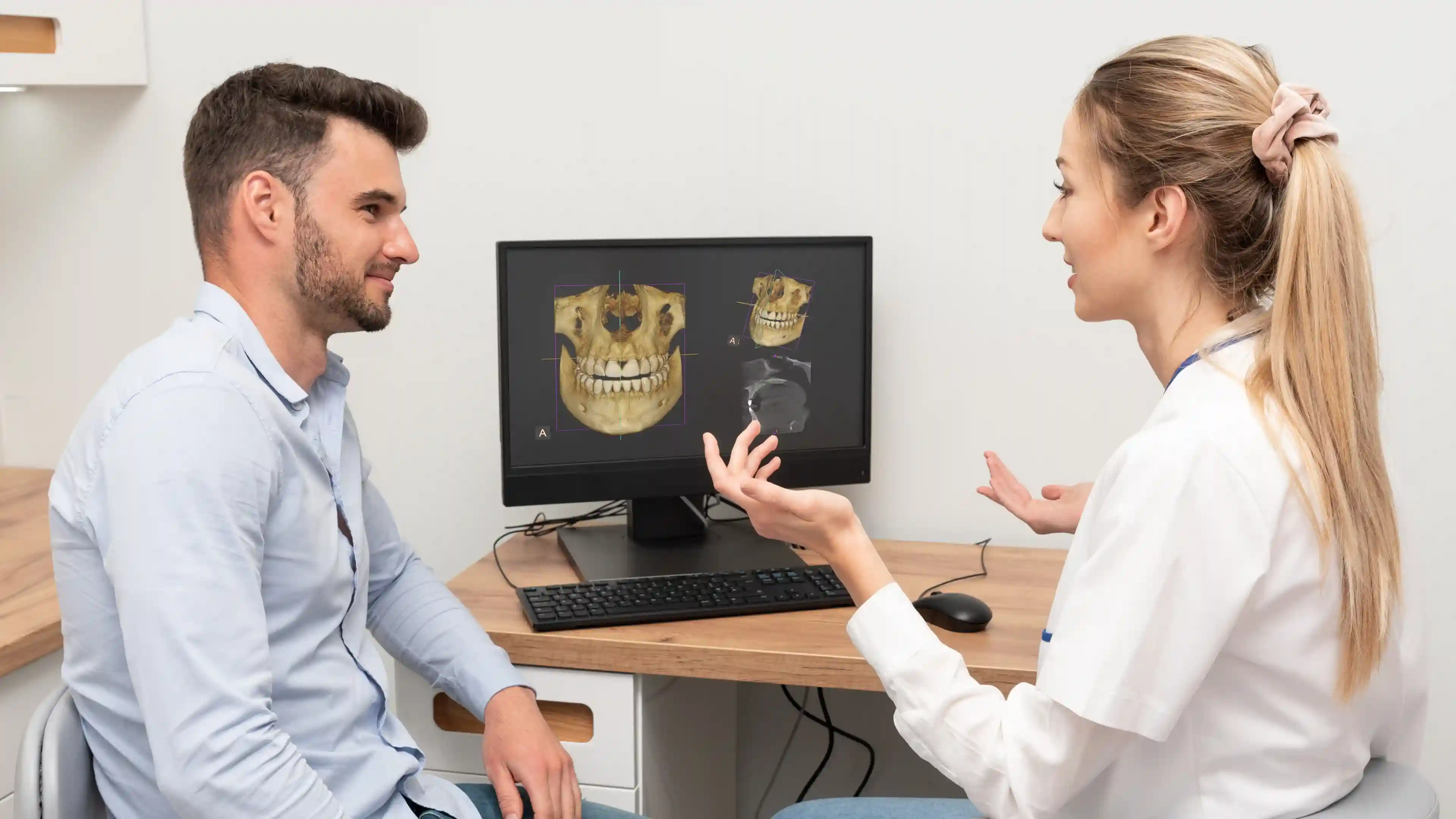
What Are the Key Benefits of 3D Dental Imaging in Dentistry?
The advantages of 3D dental imaging span improved diagnostics, enhanced treatment accuracy, and better patient communication. The ability to generate lifelike images helps clinicians plan procedures with minimal guesswork. For instance, identifying root fractures, cysts, or bone loss is far easier with dental imaging 3D than with 2D x-rays.
From an operational standpoint, 3D dental imaging software speeds up workflows and reduces patient chair time by eliminating the need for multiple scans. Patients benefit from less invasive treatment and a greater understanding of their dental condition, especially when shown their own scan results. Ultimately, the adoption of 3D imaging software dental enhances trust between patient and practitioner, reinforcing better oral care.
How Can Dentists Incorporate 3D Dental Imaging Into Routine Dental Care?
Incorporating 3D dental imaging into daily dental practice starts with acquiring a reliable CBCT system. This equipment can easily integrate with modern dental 3D imaging software, allowing dentists to view, analyze, and store patient scans digitally. Once set up, these systems can be used for routine diagnostics, surgical planning, and treatment monitoring. The integration of AI in dental applications further enhances this process by automating image analysis, detecting anomalies, and supporting clinical decision-making.
For optimal use, training is crucial. Dental teams should be well-versed in operating 3D imaging software dental, interpreting scans, and applying findings to clinical decisions. Continued education ensures that dental imaging 3D becomes a seamless part of patient care. Over time, 3D imaging evolves from being a novelty to a necessity, enhancing not only the standard of care but also the reputation of the clinic itself.
What is Cone Beam CT (CBCT)?
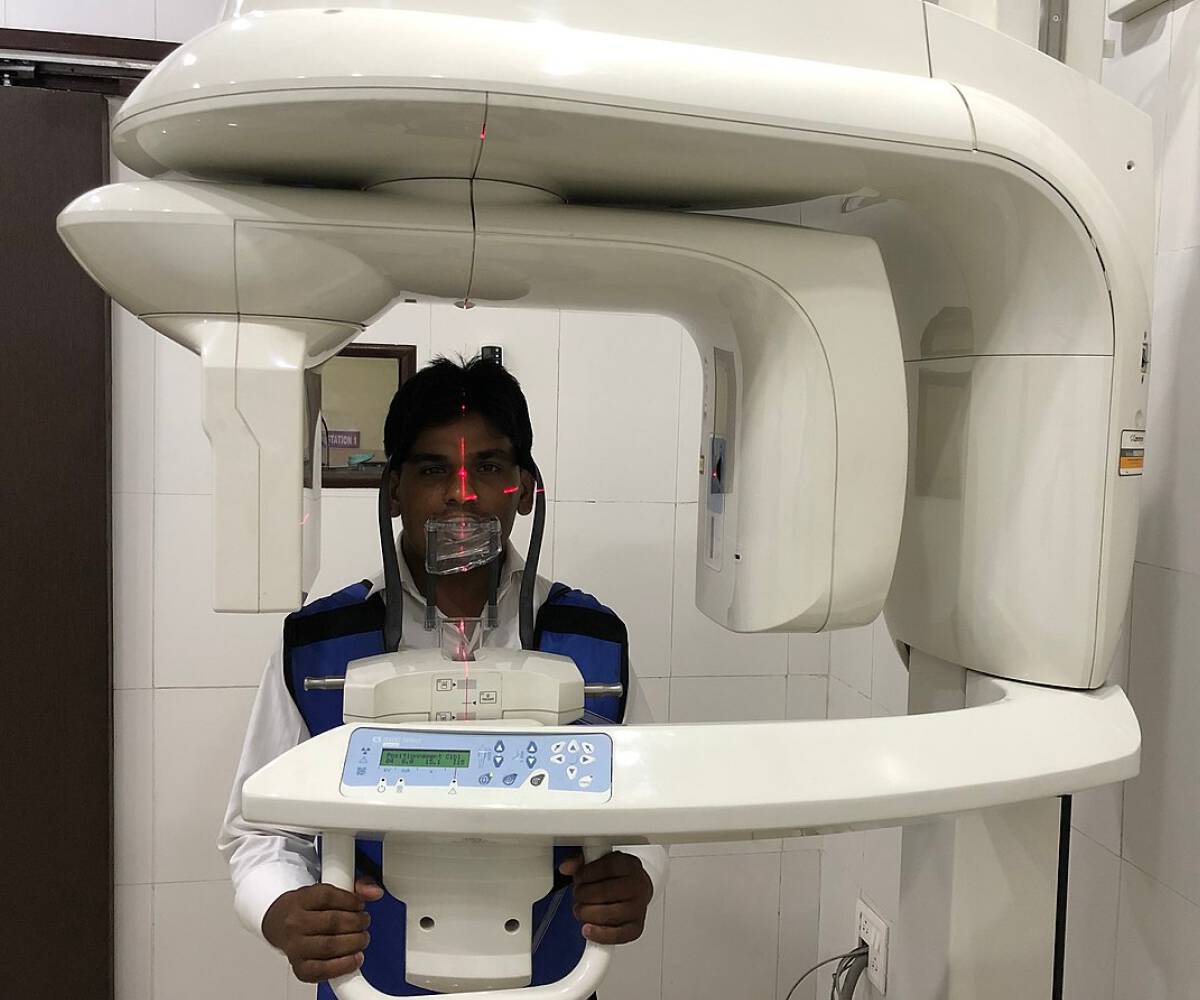
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is a type of 3D dental imaging system that rotates around the patient’s head to capture detailed scans of the teeth, jawbone, and surrounding tissues. Unlike conventional x-rays, CBCT offers dental 3D imaging with lower radiation levels and higher precision.
Typically used in implantology and surgical planning, CBCT provides accurate measurements of bone density, sinus location, and nerve paths. If you're wondering “what is 3D dental imaging”, CBCT is a prime example—offering comprehensive views that are essential for safe and successful treatments.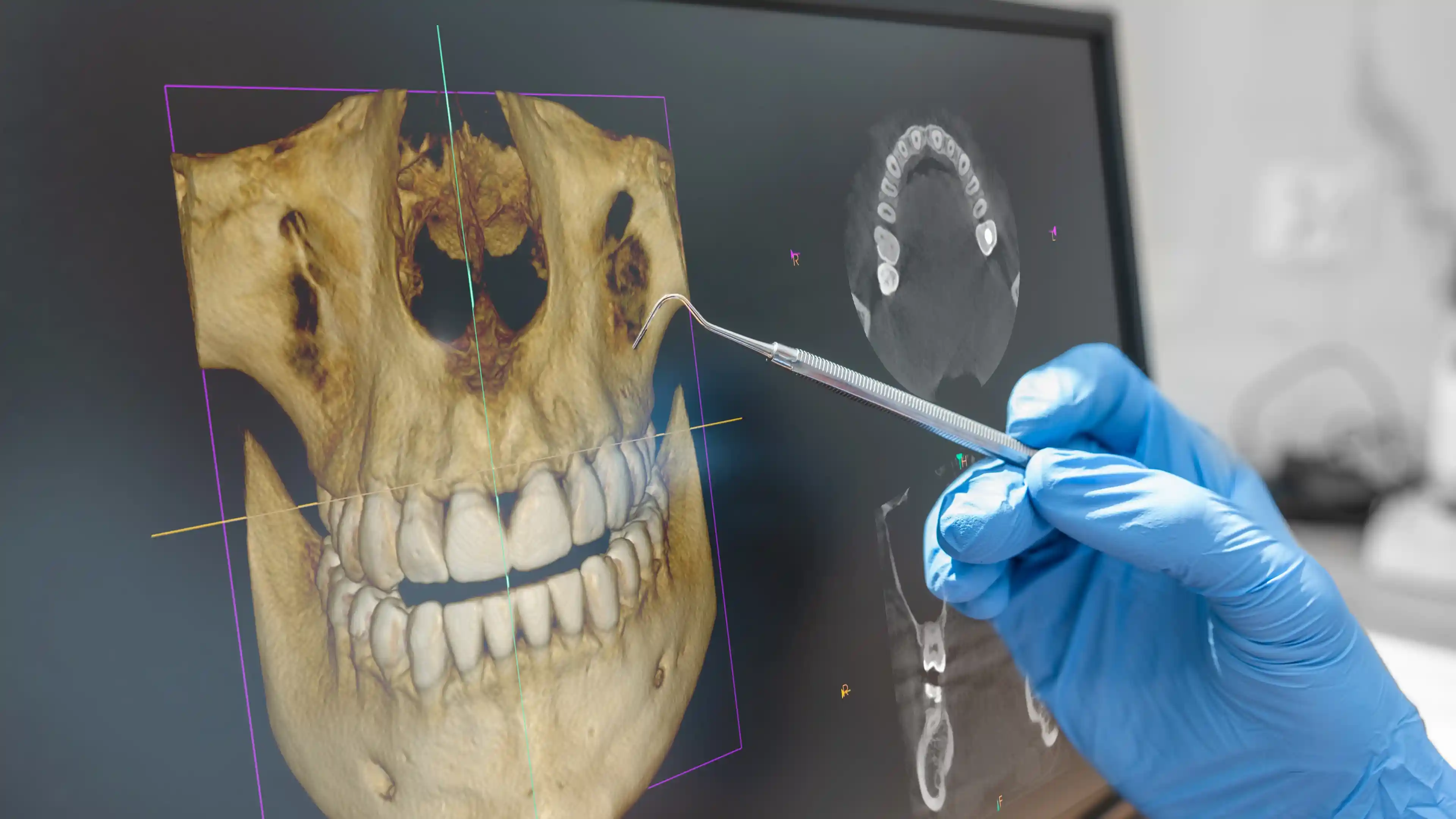
Does My Insurance Cover 3D Dental Imaging?
Insurance coverage for 3D dental imaging varies depending on your provider and treatment purpose. Many policies cover it when deemed medically necessary, such as for implant planning or evaluating jaw abnormalities. Some may refer to it as 3D radiography dental, 3D scan of teeth, or 3D dental xray in their documents.
It’s always best to verify with your insurance company whether a 3D tooth x ray or 3D scan for teeth is included in your benefits. With the rise of 3D xray technology, insurers are increasingly recognizing the value it brings to accurate diagnostics and effective treatment planning.
How Do You Benefit from 3D Dental X-Rays?
3D dental x-rays offer a full spectrum view of your oral anatomy in a single scan, reducing the need for multiple imaging sessions. These scans deliver detailed information about your teeth, jaw, nerves, and sinus cavities—crucial elements in diagnosing complex dental issues. With the help of 3D dental imaging, your dentist can identify concerns earlier and plan treatments more precisely.
This technology also increases efficiency and safety. A 3D dental scan using CBCT takes just a few seconds and exposes patients to significantly less radiation than conventional x-rays. This means a safer, faster, and more comfortable diagnostic experience for every patient.How to Do 3D Imaging?
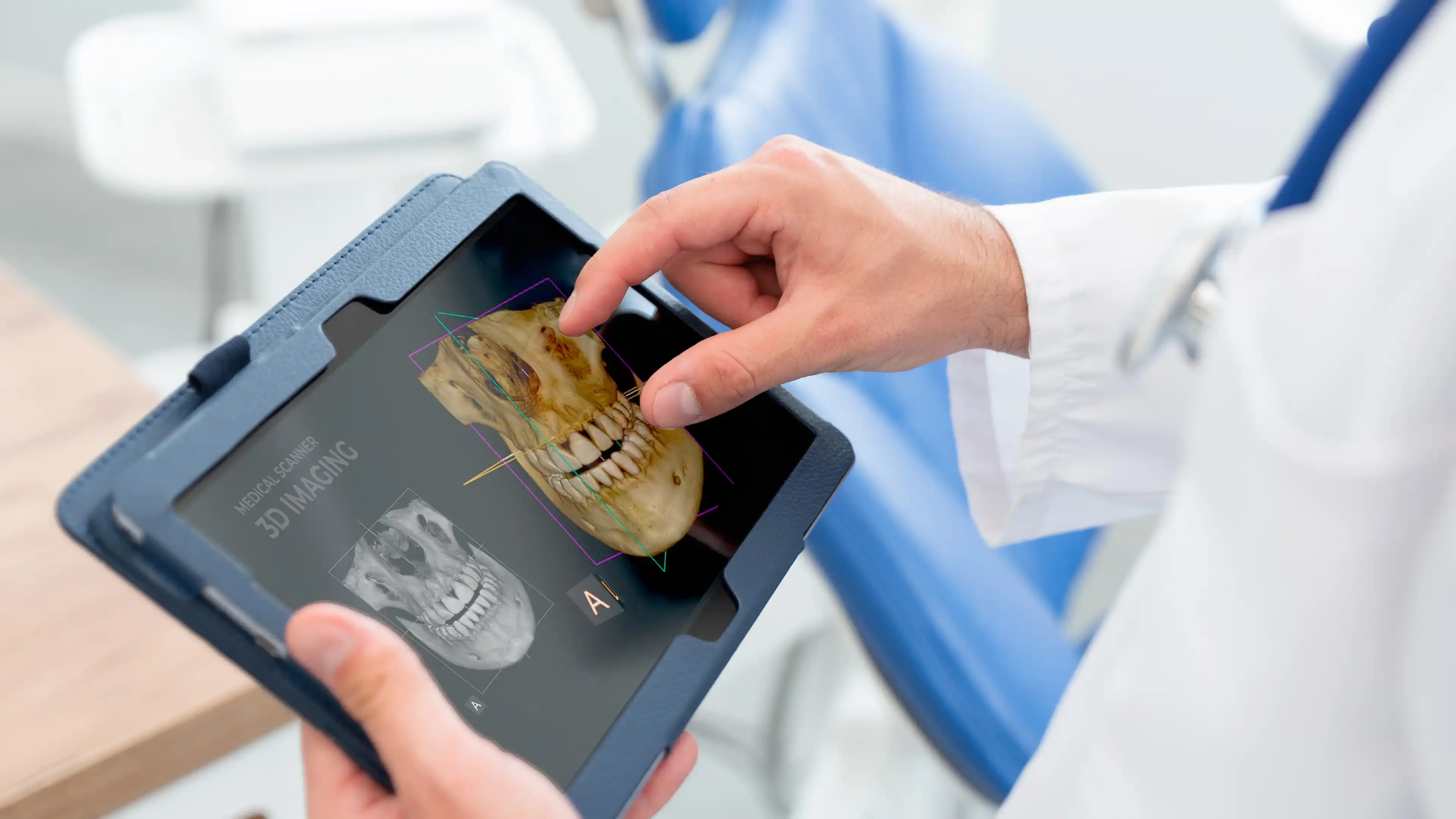
Performing 3D dental imaging involves using a CBCT scanner to rotate around the patient's head, capturing hundreds of images from multiple angles. These are then processed by dental 3D imaging software to generate a complete 3D model of the oral structures.
This scan allows dentists to navigate through layers of tissue, bone, and teeth—offering insights not possible with traditional imaging. The integration of 3D imaging software dental systems into clinics has made this process quick, reliable, and an essential part of modern diagnostics.
What is the Purpose of 3D Imaging?
The primary purpose of 3D dental imaging is to enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning. With 3D x-rays for teeth, dentists can detect fractures, abscesses, or abnormal growths that might be invisible in 2D images. These images allow for a full evaluation of the oral cavity, aiding in better decision-making.
As a result, 3D imaging in dental implantology has become standard for planning implant placement and sinus lift procedures. It ensures that implants are placed precisely, minimizing complications and improving long-term success.
Types of 3D Imaging for Dental Care
There are several types of 3D dental imaging technologies used in dentistry today:
- CBCT (Cone Beam CT): Ideal for implant planning, jaw analysis, and sinus evaluation.
- Intraoral Scanners: Used for capturing digital impressions for crowns, bridges, and aligners.
- 3D Facial Scanners: Helpful in orthodontics and maxillofacial surgery planning.
- Panoramic X-rays with 3D Options: Often integrated into general practice for quick assessments.
Each of these tools is powered by 3D dental imaging software, providing a combination of accuracy and convenience. By incorporating various forms of dental imaging 3D, clinicians can offer comprehensive and personalized care across disciplines.
FAQ
What is 3D imaging in dentistry?
It refers to the use of 3D x-ray technology to capture detailed, multi-dimensional views of a patient’s oral structures. 3D dental x-rays allow for better diagnosis and treatment outcomes.
What is the difference between 3D and CBCT?
All CBCTs are 3D, but not all 3D imaging systems use CBCT. CBCT is a specific type of 3D dental imaging used mainly for dental and maxillofacial purposes.
What is a 3D radiographic procedure?
This is a diagnostic scan using 3D x-ray teeth systems to obtain layered images of the oral cavity, revealing hidden pathologies or bone abnormalities.
What is the use of a 3D scanner in dentistry?
3D scanners are used for capturing accurate models of the teeth and jaw for diagnostics, surgical planning, and prosthetic design. They are a key part of any modern 3D dental imaging setup.



 Contact Us
Contact Us

